Geography
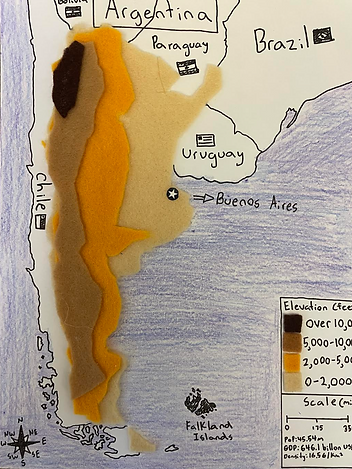
Argentina is the 2nd largest country in South America and spans half of the entire continent. Argentina is generally separated into 4 topographical regions. The Pampas, Patagonia, the lowland region of the northeast, and the northwest Andes. The Pampas is a large, fertile grassland in which the capital of the country is located. Patagonia is a steppe-like plains terrain with many mountains, glaciers, fjords, and deserts. Patagonia takes up the entire bottom part of the country. Patagonia can be compared to the Denali mountains in Alaska because of their similar mountainous terrain. The lowland region of northeast Argentina is lush forests with extensive wetlands with a mostly flat terrain. Argentina's climate ranges a lot compared to neighboring countries. The northern part of the country is warmer and has lots of rainfall. The temperature decreases until the Patagonia region, where cold temperatures exist year-round. The northwest Andes, which is the bottom of the Andes mountain range, stretches through many countries in South America. The northwest Andes are located in the west of the country. The northwest Andes are usually dry with deserts, mountains, and canyons similar to the Grand Canyon in Utah. The climate and geography a defining factors in the way of life in Argentina. The different topographical regions change daily life for local residents living in the regions.

The Pampas

Gran Chaco

Patagonia

Andes